CHAPTER XVII
Resume of the
Growth of the Gulf,
|
|
|
THE MATERIAL which has been presented in the preceding chapters has emphasized changes that have taken place in specific periods of the development of the GM&O. In this and the following chapters the over-all period of growth will be stressed. This chapter (CHAPTER XVII) is devoted to a visual and graphic portrayal the development of the road. The maps show the changes in the mileage and territory served by the company. The charts are deed to help the reader understand some of the financial and rating changes which have taken place in the period from 1920 to 1950. Figures for the four most important of those companies which have been merged into the GM&O have been presented, along with the parent GM&N-GM&O. Figures for the two other north-south railroads which operate east of the Mississippi River from the gulf ports of Mobile and/or New Orleans have been given also. In addition, comparative figures for all Southern District and Class I railroads of the United States have been given where they are available. In looking at these charts, one must bear in mind the fact that these railroads are not at all comparable in length of service, mileage, traffic density, or wealth. One must remember, also, that changes in basic circumstances for one road - e.g., the addition of more miles of lines--must be considered before quick comparisons are made. These charts do offer important information, however, when the rate of change for one company over a period of years is compared with the rate of change for another company. The reader who is interested primarily in the narrative of the history of the GM&O and its predecessors may omit the material in Chapters XVII-XIX and move directly to Chapters XX through XXIV, which are concerned with the histories of the predecessor roads and the GM&N itself, prior to 1920. 1. 1913-16. Reorganization of the New Orleans, Mobile and Chicago into the Gulf, Mobile and Northern. GM&N practically debt free as of January 1, 1917 (369 miles of main line). 2. 1918. Purchase of stock control of the Meridian and Memphis (32 miles) by the GM&N. 3. 1919. Completion of the extension from Middleton, Tennessee, to Jackson (40 miles). B. Major Changes-March, 1920, to September, 1940 1. 1920-25. Creation of a well-run, aggressively promoted, small railroad. 2. 1924. Purchase of corporate control of the Birmingham and Northwestern (49 miles) by the GM&N. (This line from Jackson, Tennessee to Dyersburg had been operated in co-operation with GM&N policy since March, 1920. I. B. Tigrett had been president of the B&NW from 1912 to 1920. ) 3. 1926. Purchase of corporate control of the Jackson and Eastern (33 miles in operation) by the GM&N. (Jackson and Eastern line rebuilt and extended about 40 miles further to reach Jackson, Mississippi, in 1927. ) 4. 1926. Acquisition of trackage rights over Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis line from Jackson, Tennessee to Paducah (145 miles) for freight service. 5. 1929. Merger of Birmingham and Northwestern, Meridian and Memphis, and Jackson and Eastern into the GM&N. 6. 1930. Purchase of stock control of the New Orleans Great Northern (263 miles) by the GM&N. 7. 1933. Change of trackage contract from NC&STL (145 miles, Jackson, Tennessee, to Paducah) to Illinois Central (113 miles) Jackson, Tennessee, to Paducah. 8. 1933. Acquisition of 99 year lease on property of reorganized New Orleans Great Northern. 9. 1935. Service begun by “The Rebel”, first Diesel electric streamlined passenger train in the South. 10. 1936. Creation of the totally owned subsidiary, Gulf Transport Company, to co-ordinate and enlarge previous highway service, both by bus and truck. 11. 1938. Cancellation of the IC trackage agreement between Jackson, Tennessee, and Paducah. 12. 1938. Tentative agreement reached to merge the GM&N and the Mobile and Ohio (1150 miles) into the Gulf, Mobile and Ohio. C. Major Changes-September, 1940, to March, 1952 1. 1940. Creation of the GM&O by merger of the GM&N and M&O. 2. 1947. Acquisition of the Alton Railroad (959 miles) and merger of its lines into the GM&O. 3. 1952. Acquisition of trackage rights over the Louisville & Nashville line from Tuscaloosa, Alabama, to Birmingham (55 miles). Cessation of use of IC and Southern Railway lines from Ruslor (Corinth) Mississippi, to Birmingham (172 miles).
|
|
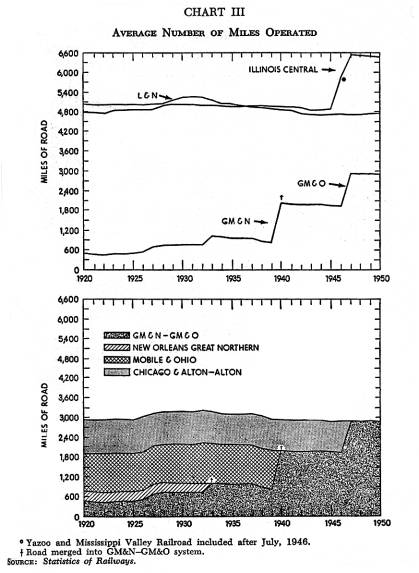
Chart III |
|
|
(The
number of miles of main track which is owned and/or operated by each
company represented) The four major companies which compose the GM&O of 1950 operated an average of 2,934 miles of line in
1920. Since that time,
various additions and subtractions have taken place in the operations of
the four companies. In
1950, however, the GM&O operated
2,898 miles, which is quite close to the 2,934 miles of the four
companies in 1920. An
appreciable amount of mileage has been added to the companies, but
abandonments and sales have held the total nearly level. The L&N mileage has declined slightly as abandonments have taken their toll. Figures for the IC show an upward trend because the early years show mileage for the IC only. As subsidiaries have been merged into the parent company, its mileage has increased substantially. |
|
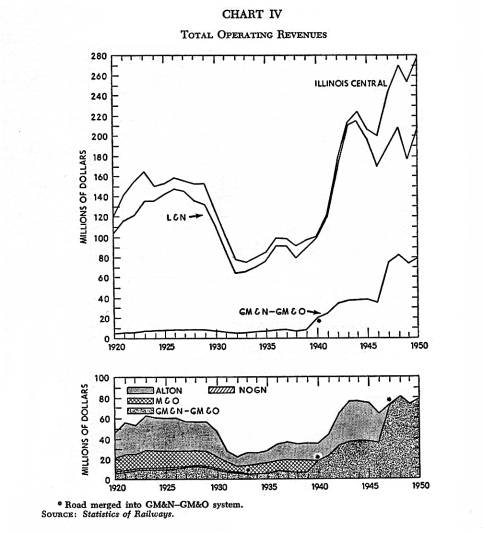
Chart IV |
|
|
(All
revenue received from operating the various railroads for transportation
purposes is included. Any
revenue which might be received from outside sources is excluded.) This
tabulation of gross operating revenues has not been adjusted to price
changes and therefore is not as valuable for long-run comparisons as it
might be otherwise. Within
any period of a few years, however, comparisons between companies will
be valid indications of changes in operating conditions or in the
availability of traffic. All of the railroads shown in the chart suffered severe losses in revenue during the depression of the 1930’s. Both the Alton and the M&O, however, suffered more severe drops in revenue than the other roads listed.
|
|
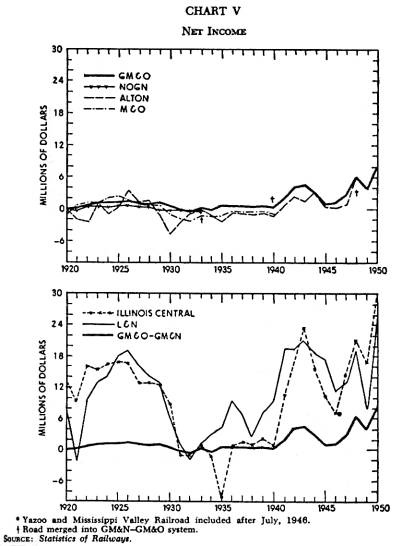
Chart V |
|
|
(Net
income figures include the total amount of profit which a company has
made in a given year.) The
net income record shows that the roads which have been merged into the
GM&N-GM&O had serious difficulties during the depression of the
1930’s.
It also indicates that the Alton had a poor record even in the
prosperous 1920’s. The prosperous condition of the GM&O since 1940 does not necessarily indicate that the merger program has been successful. Only another serious decline in business will prove conclusively that the GM&O has or has not strengthened the former roads by its merger program.
|
|
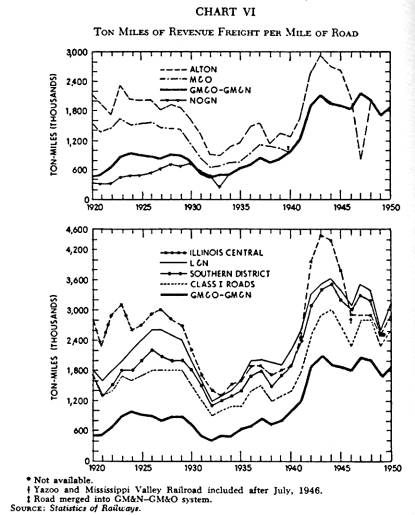
Chart VI |
|
|
(The
density of total bulk of freight traffic is shown by this chart.
This is a comparative figure which railroads use to see if business
improves or declines in a given period as compared to some other similar
period.) The GM&O of 1950 is not heavily used in comparison with national or southern district averages. Density figures in the chart above show that the GM&N of 1920 has shown decided improvement, but traffic on the road is much lighter than either the Southern or national average or that of the L&N or the IC. Traffic on the Alton sector of the line has been heavier than that on the lines south of St. Louis, but the Alton itself was below national averages prior to the merger.
|
|
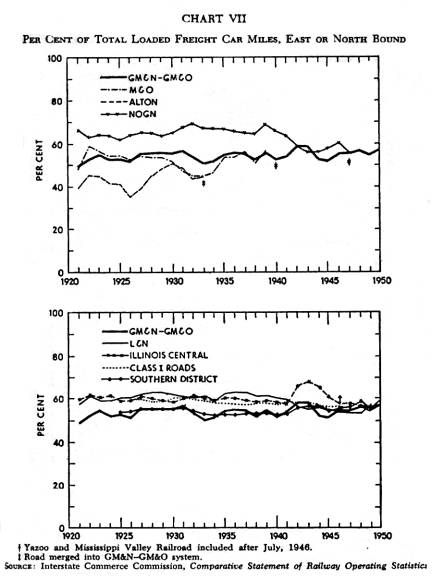
Chart VII |
|
|
(A record which shows whether or not a specific railroad is hauling approximately the same amount of tonnage in both directions, The ideal situation would be 50 per cent of loaded cars moving eastward or northward.) One
of the accepted measures of operating efficiency is the per cent of the
total loaded freight car miles which move either east or north. This is a measure which the operating department of a
railroad cannot control directly since the traffic flow is primarily
responsible for such averages. In this test the GM&N-GM&O has shown a relatively high degree of conformity to Southern and national averages. The Alton prior to World War II had a very decided bias in favor of loaded cars moving east or north, thus in effect causing the west- or south bound trains to operate with many empty cars. Both the L&N and the IC have had a tendency to operate in the same manner.
|
|
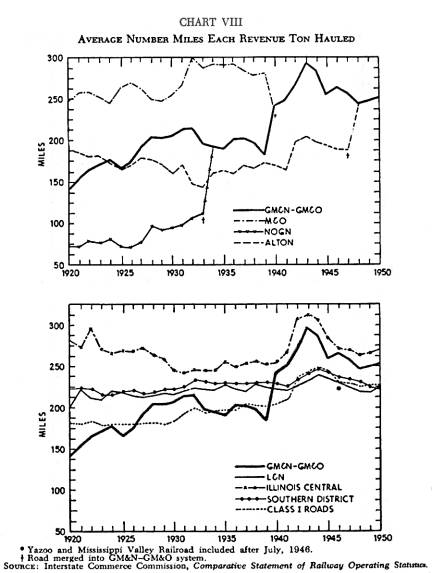
Chart VIII |
|
|
(A record which shows the average length of the haul which each railroad gets.) The GM&N-GM&O has consistently worked to obtain the longest haul possible under existing conditions. In the years from 1920 to 1931 the GM&N had increased its average from 141 miles to 212. The change of trackage rights to Paducah from the lines of the NC&STL to those of the IC caused a decrease in average haul by the year 1933. Again, the cessation of operations to Paducah over the IC in 1938 caused a decline for 1939. Since the merger of 1940 the GM&O has held a high average which was again lowered when the Alton merger took place in 1947. The current trend is upward and at present the GM&O exceeds the national and southern average as well as the average of the L&N. The IC, with its well-developed, long-line system, still exceeds the average haul of the GM&O, even though the IC average declined in 1948 with the addition of statistics from the Y&MV.
|
|
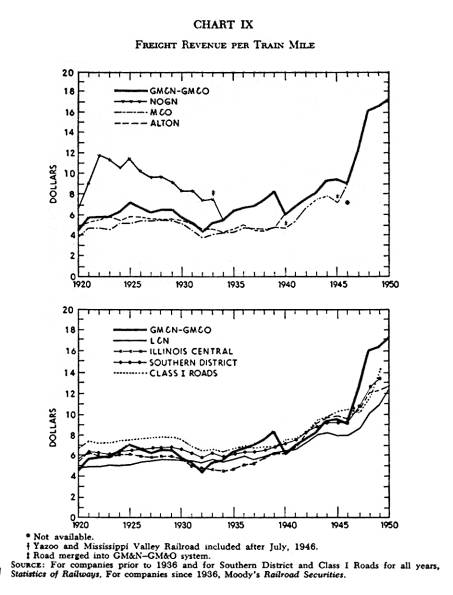
Chart IX |
|
|
(This
chart shows the amount of revenue which each railroad receives for the
work performed by an average freight train as it moves one mile.) Freight
revenue per train mile is a worthwhile indicator of operating efficiency
when the volume of traffic does not materially change from year to year.
It is impossible to compare the revenue per train mile for the
GM&N of 1920 with that of the GM&N of 1932 and thus determine
that the operating department was less efficient in 1932 than in 1920.
One can say, however, that a company with a train mile revenue
of $16.64 is more fortunate than a company with a train mile revenue of
$10.96. Much of the increase which the GM&O has shown since 1945 is due to the use of Diesel locomotives in road freight service.
|
|
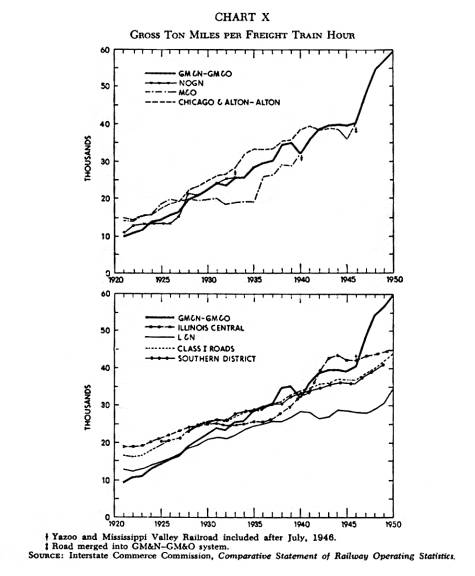
Chart X |
|
|
(This
chart shows the average number of tons of freight and freight train
equipment which is moved one mile in one hour by one freight train. Speed of trains is an important element in this record. ) There
are many indicators which can be developed that show the relative operat.
ing efficiency of railroads.
The figures for train mile operation are important evidences of
efficiency when properly interpreted.
Perhaps the most highly regarded indicator of over-all railroad
operating efficiency is gross ton miles per freight train hour. The GM&N of 1921 rated about 57 per cent of the national figure in this calculation. The GM&O of 1950 was well in advance of the national average, with its total of 59,690 ton miles being 136 per cent of the national average of 44,353 ton miles per train hour.
|
|
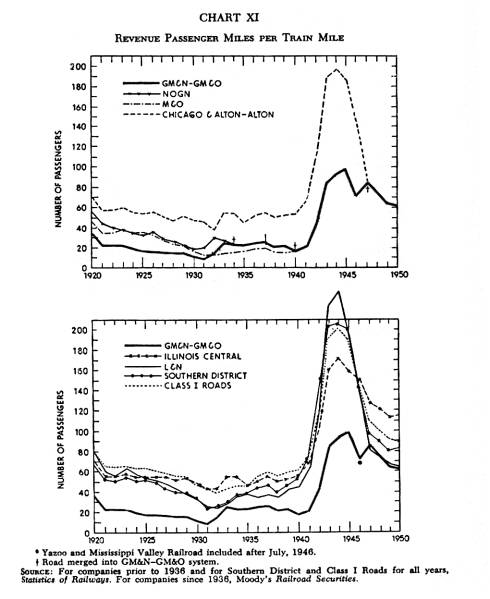
Chart XI |
|
|
(This
record shows how many paying passengers ride on the average train as it
travels one mile.) The
average number of passengers per train mile does not indicate volume directly,
but it does show that for the trains which the GM&N-GM&O has
run, patronage has been much lighter than Southern and national
averages. The Alton was once known as a “passenger” railroad and its passenger averages were much higher than those of the Southern lines of the GM&O. Addition of the Alton’s passenger business into the average of the GM&O has caused a definite increase since 1947 for the road as a whole.
|
|